Introduction
Stablecoins have exploded in popularity over the past few years, becoming a key pillar in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Unlike volatile crypto assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum, stablecoins aim to deliver price stability while preserving the benefits of digital currency. This unique hybrid model makes them essential for cross-border payments, trading, and decentralized finance (DeFi).
But with growing regulatory scrutiny and competition from central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), what does the future hold for stablecoins?
What Are Stablecoins and Why Do They Matter?
A stablecoin is a digital asset pegged to a stable value—most commonly the U.S. dollar. The goal is simple: provide the speed and programmability of blockchain transactions without the price swings of cryptocurrencies.
Why they’re important:
- Enable fast, low-cost international transfers.
- Act as an on/off ramp for crypto users.
- Reduce volatility risks in trading and lending.
Types of Stablecoins
There are three primary models, each with strengths and weaknesses:
1. Fiat-Collateralized
- Backed 1:1 by reserves in a bank.
- Examples: USDC, USDT.
- Pros: Transparent (if audited), simple to understand.
- Cons: Centralized and subject to regulatory risks.
2. Crypto-Collateralized
- Backed by volatile crypto assets over-collateralized to maintain stability.
- Example: DAI.
- Pros: Decentralized, no single point of failure.
- Cons: Complex and vulnerable during market crashes.
3. Algorithmic
- Stabilized through supply-demand algorithms, not reserves.
- Example: UST (collapsed).
- Pros: Fully on-chain, no custody risk.
- Cons: Fragile and often unsustainable.
Why Stablecoins Could Replace Wire Transfers
Traditional remittance systems are slow and costly. International transfers can take 3–5 business days and involve multiple intermediaries. Stablecoins reduce settlement time to seconds and transaction fees to a fraction of a cent.
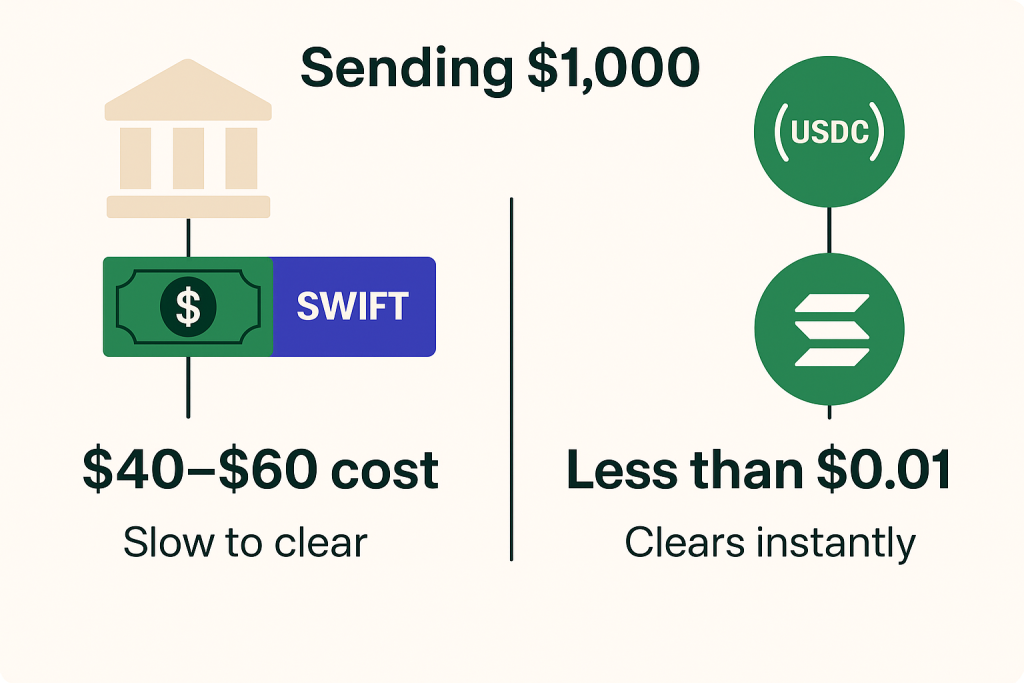
Case Study:
Sending $1,000 via SWIFT can cost $40–$60. Using USDC on a blockchain like Solana costs less than $0.01 and clears instantly.
Challenges Facing Stablecoins
While promising, stablecoins face several hurdles:
Regulatory Uncertainty
- Governments worry about money laundering, tax evasion, and systemic risk.
- The EU’s MiCA regulation and the U.S. Stablecoin TRUST Act aim to set guardrails.
Banking Partnerships
- Reserves often depend on regulated banks.
- Recent collapses like Silvergate showed how fragile these relationships can be.
CBDC Competition
- Central banks are launching digital currencies.
- Could reduce reliance on private stablecoins in payment systems.
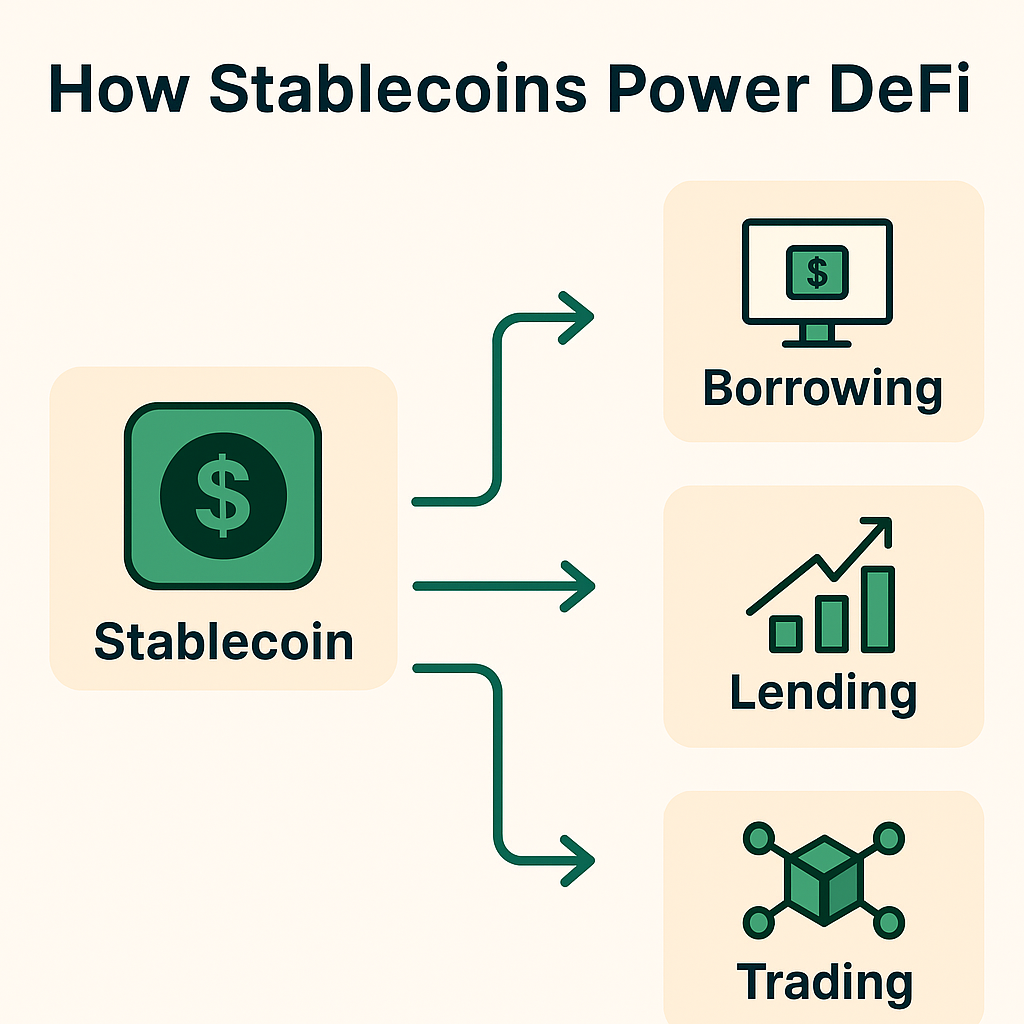
The Role of Stablecoins in DeFi
Stablecoins are the lifeblood of DeFi, powering:
- Lending & borrowing platforms like Aave.
- Yield farming and liquidity pools.
- Synthetic asset creation.
Without stablecoins, DeFi would be a volatile mess—too risky for mainstream adoption.
The Future: Regulation, Integration, and Mass Adoption
Expect the future of stablecoins to focus on:
- Full reserve audits for transparency.
- Integration with banking APIs for compliance.
- Expansion into real-world use cases (e-commerce, payroll, remittances).
Some predict that stablecoins could become the dominant form of digital money—even more used than Bitcoin.
Practical Checklist for Choosing a Stablecoin
Before using stablecoins for payments or savings, check:
- Reserves: Is it fully backed and audited?
- Issuer: Reputable company with regulatory compliance?
- Blockchain: Secure, low-fee network?
- Redemption: Easy to cash out to fiat?
